Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 CuO
CuO
Yoshii, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Akahama, Hiroshi*; Kano, Jun*; Kambe, Takashi*; Ikeda, Naoshi*
Physica C, 471(21-22), p.766 - 769, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:61.3(Physics, Applied)We have investigated the magnetic and dielectric properties of Bi CuO
CuO , which has the same chemical formula as that of the parent materials of high-Tc superconductors, R
, which has the same chemical formula as that of the parent materials of high-Tc superconductors, R CuO
CuO (R: rare earths). Magnetic measurements showed that this oxide exhibits an antiferromagnetic transition at around 40 K, owing to the localized Cu
(R: rare earths). Magnetic measurements showed that this oxide exhibits an antiferromagnetic transition at around 40 K, owing to the localized Cu spins. Dielectric constants were found to be about 100 at room temperature, which are smaller than those of R
spins. Dielectric constants were found to be about 100 at room temperature, which are smaller than those of R CuO
CuO (about 10000 at room temperature). The imaginary part of dielectric response showed the activation energy of about 0.1 eV, suggesting that the dielectric response is brought about by a transfer of Cu-3d electrons.
(about 10000 at room temperature). The imaginary part of dielectric response showed the activation energy of about 0.1 eV, suggesting that the dielectric response is brought about by a transfer of Cu-3d electrons.
Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Physica C, 471(21-22), p.662 - 665, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.82(Physics, Applied)Since the discovery of the first iron-based superconductor, various types of iron-based superconductors have been fabricated to attain higher 
 . Recently, it is reported that
. Recently, it is reported that 
 of an iron-based superconductor LaFeAsO
of an iron-based superconductor LaFeAsO F
F is enhanced to 35 K by doping hydrogen. These results imply that atoms of light elements, such as hydrogen and oxygen, penetrate into the crystal of iron-based superconductors and transform their structures into more useful ones for superconductivity. In this paper, we investigate how the light elements are doped in the iron-based superconductors by using the first-principles density functional theory. Furthermore, we evaluate the effects of doping on the crystal structures and electronic states and explore the origin of the
is enhanced to 35 K by doping hydrogen. These results imply that atoms of light elements, such as hydrogen and oxygen, penetrate into the crystal of iron-based superconductors and transform their structures into more useful ones for superconductivity. In this paper, we investigate how the light elements are doped in the iron-based superconductors by using the first-principles density functional theory. Furthermore, we evaluate the effects of doping on the crystal structures and electronic states and explore the origin of the 
 enhancements.
enhancements.
 (As,P)
(As,P)
Ishikado, Motoyuki; Kodama, Katsuaki; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Iyo, Akira*; Eisaki, Hiroshi*; Arai, Masatoshi; Shamoto, Shinichi
Physica C, 471(21-22), p.643 - 646, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.88(Physics, Applied)Superconducting gap symmetry of 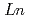 1111 system, which has the highest
1111 system, which has the highest  in iron-based superconductors, is considered to be full gap
in iron-based superconductors, is considered to be full gap 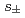 wave based on magnetic penetration depth and neutron scattering measurements. On the other hand, a line node gap symmetry is proposed in BaFe
wave based on magnetic penetration depth and neutron scattering measurements. On the other hand, a line node gap symmetry is proposed in BaFe (As,P)
(As,P) based on magnetic penetration depth and thermal conductivity measurements despite comparatively its high-
based on magnetic penetration depth and thermal conductivity measurements despite comparatively its high- (
( =30 K). Inelastic neutron scattering of BaFe
=30 K). Inelastic neutron scattering of BaFe (As,P)
(As,P) may exhibit different magnetic excitations in the
may exhibit different magnetic excitations in the  -position or
-position or  -dependence of a resonant peak from that of La1111 system. In this study, we performed inelastic neutron scattering measurement on 36g polycrystalline powder sample of optimally-doped BaFe
-dependence of a resonant peak from that of La1111 system. In this study, we performed inelastic neutron scattering measurement on 36g polycrystalline powder sample of optimally-doped BaFe (As,P)
(As,P) using Fermi chopper spectrometer 4SEASONS in J-PARC. We will discuss about the possible superconducting gap symmetry based on our inelastic neutron scattering results.
using Fermi chopper spectrometer 4SEASONS in J-PARC. We will discuss about the possible superconducting gap symmetry based on our inelastic neutron scattering results.
Shamoto, Shinichi; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kodama, Katsuaki; Ishikado, Motoyuki; Christianson, A. D.*; Lumsden, M. D.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
Physica C, 471(21-22), p.639 - 642, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)We have studied low-energy spin excitations on polycrystalline LaFeAsO F
F samples by inelastic neutron scattering. The dynamical spin susceptibility
samples by inelastic neutron scattering. The dynamical spin susceptibility  ''(
''( ) of the superconducting samples is found to be comparable to that of the magnetically ordered parent sample. On the other hand,
) of the superconducting samples is found to be comparable to that of the magnetically ordered parent sample. On the other hand,  ''(
''( ) almost vanishes at x=0.158, where the superconducting transition temperature T
) almost vanishes at x=0.158, where the superconducting transition temperature T is suppressed to 7 K. This suggests that the low energy spin excitations are closely connected with high-T
is suppressed to 7 K. This suggests that the low energy spin excitations are closely connected with high-T superconductivity. The disappearance of the spin excitations at low energy would correspond to the disappearance of the hole Fermi surface as the electron concentration increases with doping, as observed in ARPES measurements of BaFe
superconductivity. The disappearance of the spin excitations at low energy would correspond to the disappearance of the hole Fermi surface as the electron concentration increases with doping, as observed in ARPES measurements of BaFe Co
Co As
As at x=0.15. The relationship between the spin excitation and the Fermi surface will be discussed in comparison with other iron-based superconductors.
at x=0.15. The relationship between the spin excitation and the Fermi surface will be discussed in comparison with other iron-based superconductors.
Ota, Yukihiro; Machida, Masahiko; Koyama, Tomio*
Physica C, 471(21-22), p.760 - 762, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)We construct a theory of dynamical behavior in intrinsic Josephson junction stacks (IJJ's) with multi-gap superconducting layers, motivated by recent discovery rush of highly-anisotropic iron-based superconductors with a thick perovskite block layers. The theory predicts the existence of two kinds of phase modes, one of which is the Josephson plasma mode and other of which is the Leggett's mode. The IJJ's with multiple tunneling channels have a novel energy scale, inter-band Josephson coupling on each superconducting layer which generates a mass of the Leggett's mode. We discuss a cooperative phenomena induced by such a coupling in addition to capacitive and inductive couplings between the superconducting layers.
 -wave superconductors
-wave superconductorsNakai, Noriyuki; Nagai, Yuki; Machida, Masahiko
Physica C, 471(21-22), p.743 - 746, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)We have performed numerical calculations for low-lying excitations induced by a single non-magnetic impurity in a  -wave superconductor on the basis of two different frameworks. One is the Bogoliubov-de Gennes theory in real coordinates, while the other is the Born approximation in wave-number coordinates. This paper shows that these results for low-lying excitations are identical by using Fourier transformations.
-wave superconductor on the basis of two different frameworks. One is the Bogoliubov-de Gennes theory in real coordinates, while the other is the Born approximation in wave-number coordinates. This paper shows that these results for low-lying excitations are identical by using Fourier transformations.
Yamamoto, Atsushi; Yamada, Susumu; Machida, Masahiko
Physica C, 471(21-22), p.751 - 753, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)We study the dynamical properties of ultracold fermions in one-dimensional optical superlattices by using the adaptive time-dependent density matrix renormalization group method. The system is repulsive Hubbard model with an two-site periodic superlattice potential. Owing to superlattice structure, the ground-state states become the Mott-type insulating state at quarter filling and band-type insulating state at half filling, respectively. We clarify the dynamical properties of time evolution when the system is non-adiabatically changed to another lattice structure. The strongly-correlated interaction an unusual pairing of fermions induced the pair hopping process. We further address the robustness of pair hopping process and possibility of superconductivity by using sudden change of the external potential.
Machida, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki
Physica C, 471(21-22), p.659 - 661, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.82(Physics, Applied)We perform first-principles calculations with a LDA+U scheme for non-doped iron based superconductor LaFeAsO, which exhibits the antiferromagnetic ordering with an unexpected low magnetic moment compared to the one predicted by the standard first-principles calculation. Consequently, we find two stable electronic structures, one of which has the high magnetic moment  2.0
2.0 
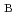 equivalent with the previous standard calculation results, and another of which reproduces the low magnetic moment
equivalent with the previous standard calculation results, and another of which reproduces the low magnetic moment  0.3
0.3 
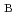 as obtained experimentally. The former is more stable in
as obtained experimentally. The former is more stable in  =0, whereas the latter becomes preferable in an intermediate
=0, whereas the latter becomes preferable in an intermediate  range. Moreover, the latter well explains anomalous features such as in-plane high anisotropy in magnetic excitation and transport as observed experimentally.
range. Moreover, the latter well explains anomalous features such as in-plane high anisotropy in magnetic excitation and transport as observed experimentally.